How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, covering everything from understanding regulations and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial photography. We’ll explore the essential components of a drone, the steps involved in pre-flight preparation, and the nuances of controlling its movements.
Whether you’re a beginner taking your first steps into the world of drones or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies with ease and responsibility.
From understanding the fundamental flight controls to utilizing advanced features like waypoint navigation and autonomous flight modes, we will provide clear explanations and practical guidance. We also address crucial aspects such as drone maintenance, troubleshooting, and legal considerations, ensuring you can operate your drone safely and legally. This guide aims to provide a complete understanding of drone operation, allowing you to confidently explore the exciting possibilities of aerial technology.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and prioritizing safety. This section details legal requirements, safety procedures, and pre-flight checks crucial for safe drone operation.
Drone Regulations by Region
Drone laws vary significantly across countries and regions. Some jurisdictions require registration, licensing, or specific flight restrictions. Always research and comply with the regulations in your area before flying. Failure to do so can result in fines or legal repercussions.
| Country/Region | Licensing Requirements | Registration Requirements | Flight Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Depending on the weight and intended use, registration with the FAA might be required. Specific certifications may be needed for commercial operations. | Registration is mandatory for drones weighing over 0.55 pounds (250 grams). | Restrictions on flying near airports, over crowds, and at night. Specific airspace restrictions are enforced using the B4UFLY app. |
| Canada | Pilot certification is required for commercial operations. Recreational pilots must follow Transport Canada guidelines. | Registration is required for drones weighing over 250 grams. | Similar restrictions to the US exist, including proximity to airports and populated areas. |
| United Kingdom | The Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) Artikels drone regulations. Registration and operator competency are key aspects. | Registration is required for most drones. | Restrictions on flying near airports, crowds, and over populated areas. Height restrictions are also in place. |
Pre-Flight Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight check is essential to ensure safe and successful flights. This minimizes the risk of accidents and protects both the drone and its surroundings.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning how to safely and effectively control your drone is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone found at DroneFair. This guide covers everything from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, ensuring you’re well-prepared for your next flight.
- Check battery charge levels and ensure batteries are in good condition.
- Inspect propellers for damage or wear.
- Verify that all components are securely attached.
- Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU.
- Check weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation, visibility).
- Review local flight regulations and airspace restrictions.
- Plan your flight path and ensure it’s safe and legal.
Post-Flight Procedures
Post-flight procedures are equally important for maintaining the drone and ensuring future safe operations. These steps help prolong the drone’s lifespan and prevent unexpected issues.
- Power down the drone and remove the battery.
- Inspect the drone for any damage.
- Clean the drone’s body and propellers.
- Store the drone and its accessories in a safe, dry place.
- Download and review flight logs.
Drone Components and Functionality
Understanding the individual components of a drone and their interaction is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section details the key components and their functions within the drone’s system.
Main Drone Components
A typical drone consists of several interconnected components working in harmony. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s ability to fly and capture data.
- Motors: Provide the power to spin the propellers, generating thrust for flight.
- Propellers: Convert motor rotation into thrust, enabling lift and maneuverability.
- Battery: Provides the electrical power for all drone components.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, responsible for processing sensor data and controlling the motors.
- GPS Module: Enables precise positioning and navigation, crucial for autonomous flight modes.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos.
- Gimbal (optional): Stabilizes the camera, ensuring smooth footage.
- Radio Transmitter/Receiver: Allows the pilot to control the drone remotely.
Drone Flight Controller Diagram
A simplified diagram of a drone’s flight controller would show its central processing unit (CPU) receiving input from various sensors (accelerometer, gyroscope, barometer, GPS). The CPU processes this data and sends signals to the Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs), which regulate the speed of each motor, thus controlling the drone’s movements. The data flow is continuous and allows for real-time adjustments in response to changes in the drone’s environment and pilot input.
Drone Propeller Types
Different propeller designs impact flight performance. Factors such as pitch, diameter, and number of blades influence thrust, speed, and efficiency. For example, larger diameter propellers generally provide more lift but may reduce speed, while a higher pitch propeller results in increased speed but potentially reduced lift.
Pre-Flight Preparations and Procedures
Proper pre-flight preparation is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This involves several key steps to ensure everything is functioning correctly and that the flight environment is suitable.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, a thorough checklist ensures all systems are ready. This minimizes risks and maximizes the chances of a successful flight.
- Charge the drone’s battery to the recommended level.
- Check the weather conditions – avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow.
- Inspect the drone for any damage, paying close attention to the propellers and body.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU.
- Update the drone’s firmware if necessary.
- Check the GPS signal strength.
- Verify that all components are securely attached.
- Plan your flight path and ensure it is within legal and safe limits.
- Inform relevant authorities if required.
Essential Items for Drone Pilots
Carrying a few essential items can significantly enhance safety and preparedness during drone operations.
- Spare batteries
- Propeller removal tool
- Screwdriver set
- First-aid kit
- Portable charger
- Sunscreen and hat
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers

Understanding basic flight controls is essential for safe and effective drone operation. This section Artikels the fundamental controls and maneuvers.
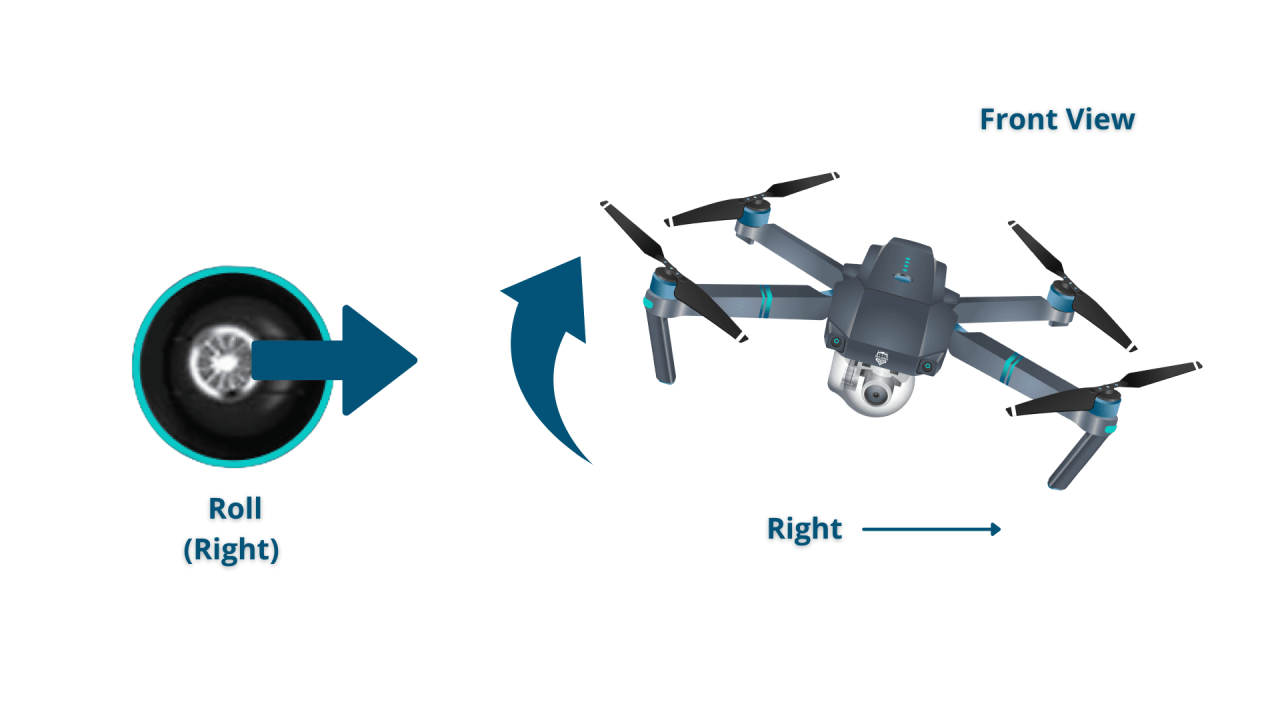
Basic Flight Controls
Most drones use two control sticks. One typically controls altitude (throttle) and forward/backward movement (pitch), while the other controls left/right movement (roll) and rotation (yaw).
| Control Stick Movement | Drone Response |
|---|---|
| Left stick forward | Drone moves forward |
| Left stick backward | Drone moves backward |
| Left stick left | Drone moves left |
| Left stick right | Drone moves right |
| Right stick forward | Drone increases altitude |
| Right stick backward | Drone decreases altitude |
| Right stick left | Drone rotates left (yaw) |
| Right stick right | Drone rotates right (yaw) |
Emergency Landing Procedure, How to operate a drone
In case of a malfunction or loss of control, a controlled emergency landing is crucial. This involves prioritizing a safe landing location and gently bringing the drone down.
- Assess the situation and identify a safe landing area.
- Slowly lower the drone’s altitude using the right stick.
- Maintain control of the drone’s orientation.
- Once close to the ground, gently set the drone down.
Advanced Flight Techniques and Features

Many modern drones offer advanced flight features and techniques that enhance capabilities and simplify operation. Understanding these features can significantly improve your drone flying experience.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Successfully piloting a drone requires careful attention to detail, and a great resource for learning these techniques is available at how to operate a drone. This website offers comprehensive guidance on all aspects of drone operation, ensuring safe and responsible flight practices.
Ultimately, proficient drone operation is a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical experience.
Waypoint Navigation and Autonomous Flight Modes
Waypoint navigation allows you to pre-program a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously. This is useful for complex shots or situations where precise control is needed. Autonomous flight modes, such as “follow me” or “point of interest,” further enhance the drone’s capabilities, allowing for creative shots and hands-free operation.
Drone Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of autonomy and control. GPS mode relies on satellite signals for precise positioning, while attitude mode relies on onboard sensors for orientation and movement. Understanding the differences is essential for selecting the appropriate mode for different flying conditions and tasks.
Advanced Features: Follow Me and Point of Interest
The “Follow Me” mode allows the drone to automatically track a moving subject, keeping it centered in the frame. “Point of Interest” mode enables the drone to orbit a specific point, allowing for dynamic shots and perspectives. These features enhance creativity and reduce the need for manual control during specific maneuvers.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding both drone operation and photography techniques. This section provides guidance on optimizing image and video quality.
Camera Settings for Optimal Results
Adjusting camera settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture is crucial for achieving the desired image quality. For example, a lower ISO reduces noise in low-light conditions, while a faster shutter speed freezes motion and prevents blurring.
Composition Techniques for Stunning Aerial Shots
Composition is key to creating compelling aerial imagery. Consider using the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry to create visually appealing shots.
- Rule of thirds: Place key elements off-center for a more dynamic composition.
- Leading lines: Use natural lines to guide the viewer’s eye through the image.
- Symmetry: Create balanced and harmonious compositions using symmetrical elements.
- Perspective: Utilize altitude and angles to create unique and dramatic perspectives.
Common Issues and Solutions
Common issues include blurry footage (due to improper shutter speed or wind), overexposed or underexposed images (due to incorrect ISO or aperture settings), and shaky video (due to lack of gimbal stabilization or windy conditions).
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring your drone remains in optimal condition and extends its lifespan. This section covers routine maintenance and troubleshooting common issues.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
Regularly inspect your drone for damage, clean the propellers and body, and check the battery health. Firmware updates should also be performed regularly to ensure optimal performance and access to new features.
Cleaning and Storage
Clean your drone after each flight to remove dirt and debris. Store it in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent damage to the battery and other components.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Common malfunctions include battery issues (low charge, damage), motor problems (unbalanced propellers, motor failure), and GPS signal loss. Troubleshooting often involves checking connections, replacing faulty components, and ensuring proper calibration.
Replacing Damaged Components
Replacing damaged components, such as propellers, motors, or batteries, requires careful attention to ensure proper installation and functionality. Always consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of the key aspects involved, from pre-flight checks and safety procedures to advanced flight techniques and post-flight maintenance. Remember that continuous learning and responsible piloting are essential for ensuring safe and enjoyable flights. As drone technology continues to evolve, staying updated on the latest regulations and best practices will remain crucial.
By adhering to the principles Artikeld in this guide, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while prioritizing safety and responsible operation.
Essential FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS, automatic return-to-home functions, and obstacle avoidance features are ideal for beginners.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions, ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge.
What should I do if my drone loses signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home function that will automatically bring the drone back to its starting point. If this fails, try to manually regain control; if that fails, wait for the drone to land.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibration is usually needed after a crash or significant impact. It’s good practice to calibrate before each flight, especially if you are flying in a new location.
